NMP:Innovations
Bobo (Обговорення • внесок) |
Bobo (Обговорення • внесок) |
||
| Рядок 3: | Рядок 3: | ||
== {{PAGENAME}} == | == {{PAGENAME}} == | ||
| − | <div class="descr"> | + | <div class="descr">Department's<br>innovations</div> |
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| − | === | + | === Our innovations === |
<div class="striphash"> | <div class="striphash"> | ||
| − | * [[# | + | * [[#The system of fast solution exchange in electrophysiological experiments on Xenopus oocytes]] |
| − | * [[# | + | * [[#The system of fast application of the solutions with controlled temperature in patch-clamp experiments]] |
| − | * [[# | + | * [[#Miniature valve for opening and closing of the perfusing solution flow]] |
| − | * [[# | + | * [[#Chamber for combining tesiometric and fluorimetric measurements in multicellular smooth muscle strips]] |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | === | + | === The system of fast solution exchange in electrophysiological experiments on ''Xenopus'' oocytes === |
{| class="dbltbl" | {| class="dbltbl" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | [[File:Noga.jpg|220px]]<br> <small> | + | | [[File:Noga.jpg|220px]]<br> <small>Image of real operational system</small> |
| − | | [[File:Noga2.png|300px]]<br> <small> | + | | [[File:Noga2.png|300px]]<br> <small>System's schematic drawing</small> |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | The oocyte with microelectrodes impaled is positioned on a miniature platform made on the tip of acrylic holder (base). The platform is able to carry a microvolume of the solution around the oocyte, whilst the design of the holder provides electrical continuum for connecting the grounding electrode. The miniature valve enables suction of the new solution into the holder. To replace the solution around the oocyte with the new one, the platform is immersed into the solution-containing chambers placed on a turning table. After immersion the valve for a short time opens, and new solution is aspirated into the holder, after which the platform is taken out of the chamber. | |
| − | === | + | === The system for fast application of the solutions with preset temperature in patch-clamp experiments === |
{| class="dbltbl" | {| class="dbltbl" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | [[File:TemprPuffer2.jpg|250px]]<br> <small> | + | | [[File:TemprPuffer2.jpg|250px]]<br> <small>Image of real operational system</small> |
| − | | [[File:TemprPuffer.png|230px]]<br> <small> | + | | [[File:TemprPuffer.png|230px]]<br> <small>System's schematic drawing</small> |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | The system consists of reservoirs containing different solutions, flexible plastic tubes connecting them to the common outflow, and the block of electronic valves controlling the passage of the respective solution through the tube. The portions of the tubes between valves and common outflow pass through water jackets with different preset temperatures. The common outflow is positioned in close proximity to the investigated cell. The opening of certain valve causes a flow of the corresponding solution having the temperature of water jacket that it passes through to instantly wash the cell. The system was developed to study the temperature-sensitive channels of the TRP family. | |
| − | === | + | === Miniature valve for opening and closing of the perfusing solution flow === |
{| class="dbltbl" | {| class="dbltbl" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | [[File:Valve.png|400px]]<br> <small> | + | | [[File:Valve.png|400px]]<br> <small>Schematic drawing</small> |
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | The valve is made of an acrylic glass base, in which T-shape openings are drilled. Through the opening that passes through the whole base, an elastic tube made of silicone rubber is pulled through. This tube can be compressed by a plastic pusher located in a perpendicular opening, enabling termination of solution flow through the tube. The movement of pusher is driven by a solenoid through a flexible photographic cord. The small size of the valve and the possibility of its remote control by means of flexible photographic cord allows the valve to be positioned in a places of electrophysiological setup with limited access. | |
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[uk:NMP:Методи]] | ||
Версія за 18:22, 22 березня 2018
Innovations
innovations
Our innovations
- #The system of fast solution exchange in electrophysiological experiments on Xenopus oocytes
- #The system of fast application of the solutions with controlled temperature in patch-clamp experiments
- #Miniature valve for opening and closing of the perfusing solution flow
- #Chamber for combining tesiometric and fluorimetric measurements in multicellular smooth muscle strips
The system of fast solution exchange in electrophysiological experiments on Xenopus oocytes
 Image of real operational system |
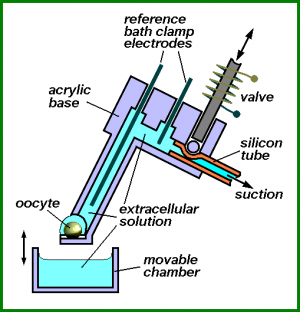 System's schematic drawing |
The oocyte with microelectrodes impaled is positioned on a miniature platform made on the tip of acrylic holder (base). The platform is able to carry a microvolume of the solution around the oocyte, whilst the design of the holder provides electrical continuum for connecting the grounding electrode. The miniature valve enables suction of the new solution into the holder. To replace the solution around the oocyte with the new one, the platform is immersed into the solution-containing chambers placed on a turning table. After immersion the valve for a short time opens, and new solution is aspirated into the holder, after which the platform is taken out of the chamber.
The system for fast application of the solutions with preset temperature in patch-clamp experiments
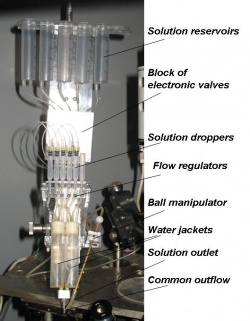 Image of real operational system |
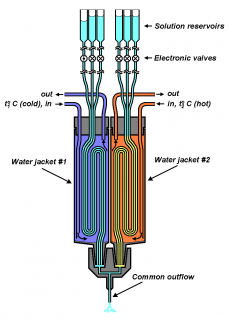 System's schematic drawing |
The system consists of reservoirs containing different solutions, flexible plastic tubes connecting them to the common outflow, and the block of electronic valves controlling the passage of the respective solution through the tube. The portions of the tubes between valves and common outflow pass through water jackets with different preset temperatures. The common outflow is positioned in close proximity to the investigated cell. The opening of certain valve causes a flow of the corresponding solution having the temperature of water jacket that it passes through to instantly wash the cell. The system was developed to study the temperature-sensitive channels of the TRP family.
Miniature valve for opening and closing of the perfusing solution flow
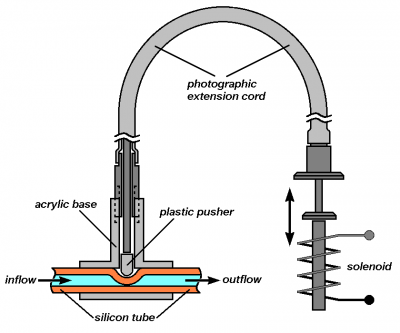 Schematic drawing |
The valve is made of an acrylic glass base, in which T-shape openings are drilled. Through the opening that passes through the whole base, an elastic tube made of silicone rubber is pulled through. This tube can be compressed by a plastic pusher located in a perpendicular opening, enabling termination of solution flow through the tube. The movement of pusher is driven by a solenoid through a flexible photographic cord. The small size of the valve and the possibility of its remote control by means of flexible photographic cord allows the valve to be positioned in a places of electrophysiological setup with limited access.

